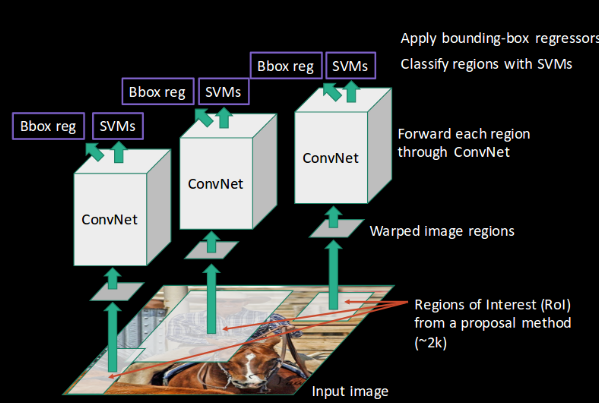
R-CNN
Prerequisites:
- Pretrained CNN is finetuned on our data
- Selective search algorithm (segmentation $\Rightarrow$ the similar regions are combined to form a larger segments (based on color similarity, texture similarity, size similarity)
Workflow:
- Propose category-independent ROIs using a selective search algorithm ($\approx2000$ regions are proposed)
- ROIs are warped to have a fixed size so that they can match the CNN input size
- Run CNN forward propagation for each warped region
- Output feature vectors are then used in a binary SVM trained for each class independently to classify objects and background
- To reduce localisation errors a regression model is trained to correct predicted bounding boxes. The linear regression model learns scale-invariant transformation between two centers and log-scale transformation between widths and heights.
Disadvantages:
- Very slow ($2000$ proposals $\Rightarrow$ for $N$ images produces $ 2000N $ ROIs)
- It is combination of three models
Fast R-CNN
Instead of running a CNN 2000 times per image Fast R-CNN pools CNN features corresponding to each region proposal.
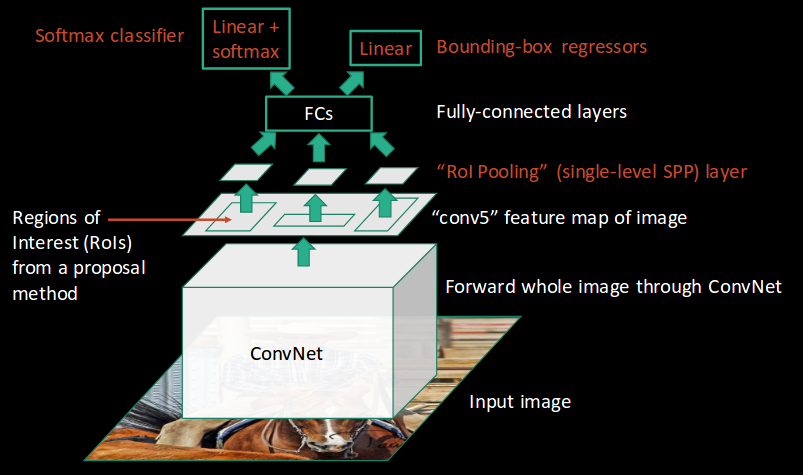
ROI poolling layer is used to convert proposed regions to regions of fixed size. Finally, these regions are passed to fully connected network which classify them and as well as return the bounding boxes using softmax and linear regression (as we saw it in RCNN) layer simultaneously.
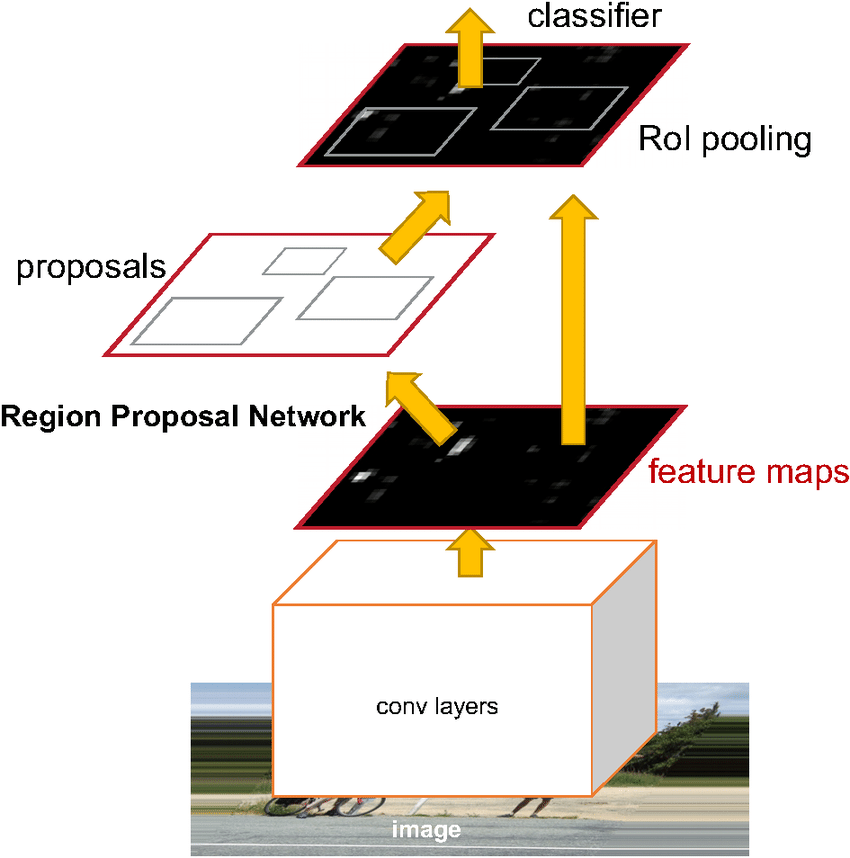
Faster R-CNN
Faster R-CNN introduces Region Proposal Network (RPN). It’s purpose is to extract all the regions of interest (ROIs). RPN is based on idea of anchor boxes: at each position of output feature map 9 (3 sizes and 3 shapes) anchor boxes are generated. To generate labels for training RPN IoU of all anchor boxes against all the ground truth boxes is calculated.
After RPN proposed regions are in different sizes.